第5章 异常
学习目标
- 了解异常的概念,能够说出什么是异常
- 了解什么是运行时异常和编译时异常,能够说出运行时异常和编译时异常的特点
- 了解异常的产生及处理,能够说出处理异常的5个关键字
- 掌握try...catch语句和finally语句的使用,能够使用try…catch语句和finally语句处理异常
- 掌握throws关键字的使用,能够使用throws关键字抛出异常
- 掌握throw关键字的使用,能够使用throw关键字抛出异常
- 掌握如何自定义异常,能够编写自定义异常类
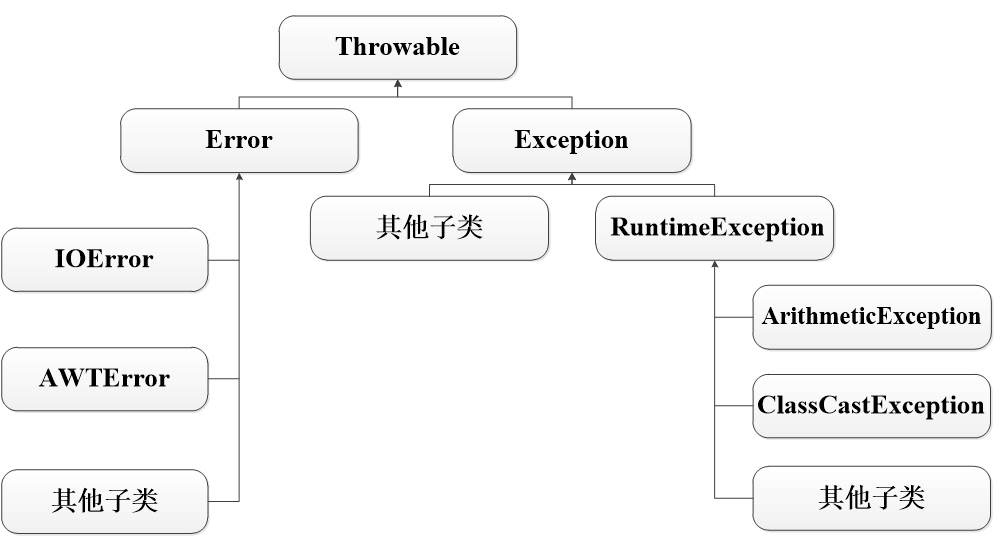
1. 什么是异常
exception 英 [ɪkˈsepʃn]例外; 异常
Java中的异常是指Java程序在编译或运行时可能出现的错误或非正常情况,比如在程序中试图打开一个根本不存在的文件,在程序中除0等。
throw 英 [θrəʊ] 抛出
able 英 [ˈeɪbl] 可
package cn.ls.ch05;
/*
* 空指针 null 空对象调用方法
* 索引越界异常 超过了数组的边界
* 数字运算异常
* 异常: 程序出现了非正常情况
* 特点:
* 1.异常信息以红色字体打印在控制台
* 2.会影响后续代码的执行--JVM非正常停止
**/
public class Ex01_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
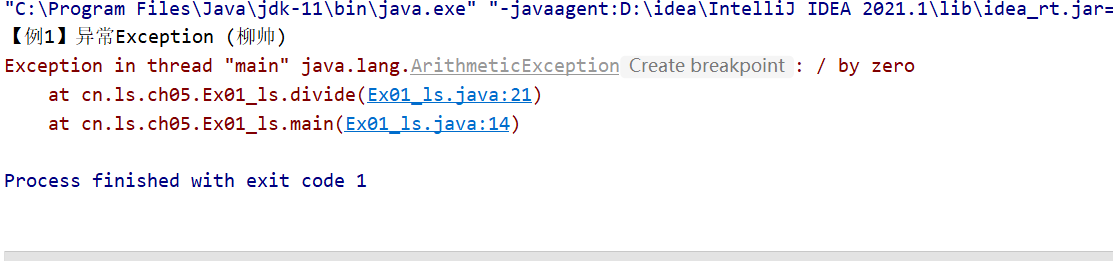
System.out.println("【例1】异常Exception (柳帅)");
int result = divide(4, 0); // 调用divide()方法,第2个参数为0
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("后续代码...");
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除
public static int divide(int x, int y) {
int result = x / y; // 定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; // 将结果返回
}
}
package cn.ls.ch05;
/*
* Throwable
* 1.Error
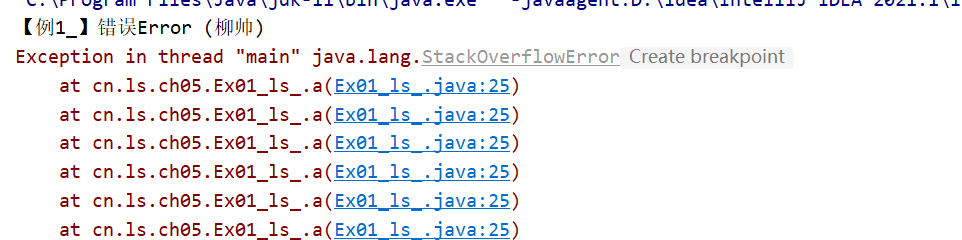
* 重大错误
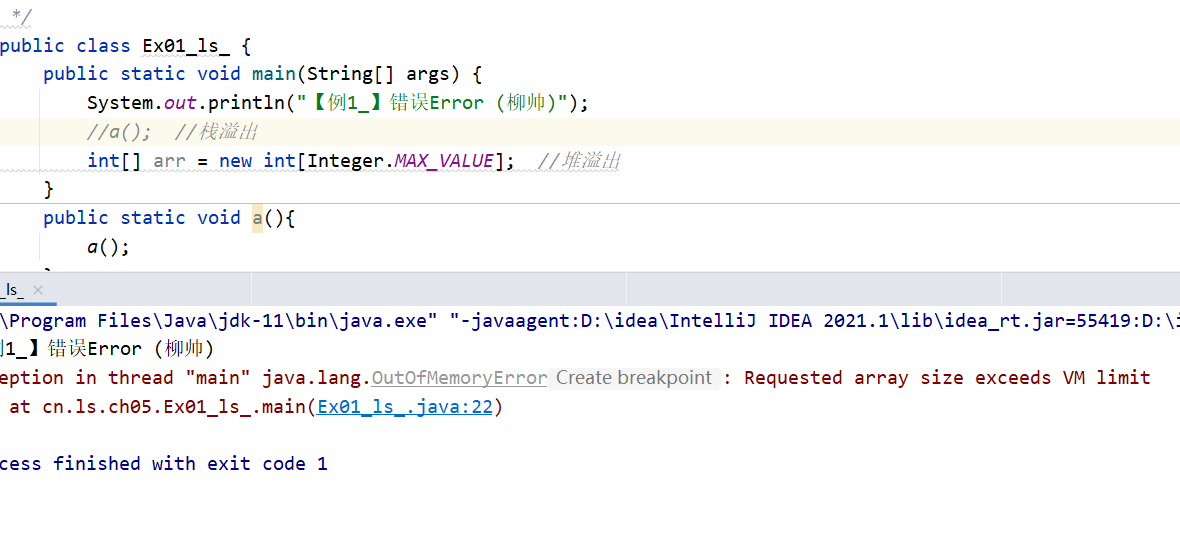
* StackOverflowError 栈溢出
* OutOfMemoryError 堆溢出
* 2.Exception
* RuntimeException 运行时异常
* 除了RuntimeException以为 编译期异常
* 抛异常:
* 创建了异常对象,阻止程序运行,以红色字体将异常信息打印在控制台
* 异常信息:
* 异常类的描述
* 出现异常的原因
* 异常出现的位置
*/
public class Ex01_ls_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例1_】错误Error (柳帅)");
a(); //栈溢出
int[] arr = new int[Integer.MAX_VALUE]; //堆溢出
}
public static void a(){
a();
}
}
Throwable类的常用方法
| 方法声明 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| String getMessage() | 返回异常的消息字符串 |
| String toString() | 返回异常的简单信息描述 |
| void printStackTrace() | 获取异常类名和异常信息,以及异常出现在程序中的位置,把信息输出在控制台。 |
2. 运行时异常和编译时异常
编译时异常
在实际开发中,经常会在程序编译时产生异常,这些异常必须要进行处理,否则程序无法正常运行,这种异常被称为编译时异常,也称为checked异常。
在Exception类中,除了RuntimeException类及其子类(运行时异常),Exception的其他子类都是编译时异常。
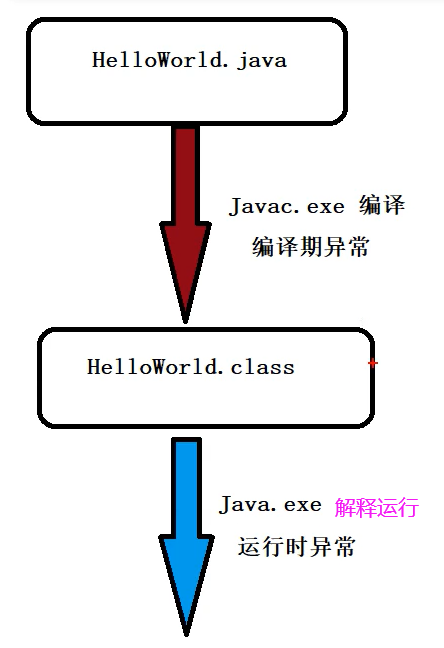
处理编译时期的异常有两种方式:
- (1)使用try…catch语句对异常进行捕获处理。
- (2)使用throws关键字声明抛出异常,调用者对异常进行处理。
throes 英 [θrəʊz] 抛
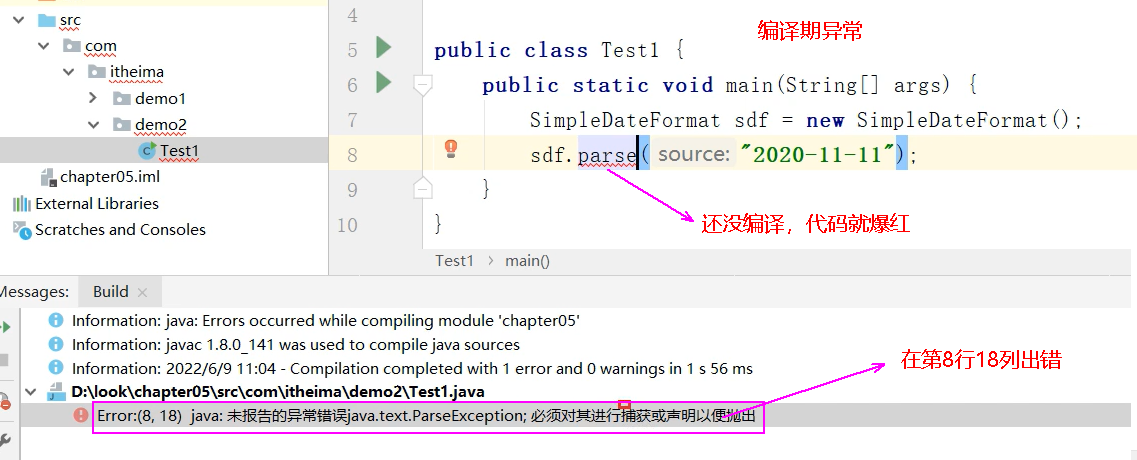
package cn.ls.ch05;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
/*
* 编译期异常:
* 编译期出现的,必须做处理,否则程序无法执行。
* 处理方式:
* 1. 捕获异常 try catch
* 2. 声明抛出异常 throws
*/
public class Ex01_ls_1 {
// 1. 捕获异常 try catch
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例1_1】编译时异常的处理方式1 捕获 (柳帅)");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
try {
sdf.parse("2020-11-11");
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 2. 声明抛出异常 throws
/* public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
System.out.println("【例1_1】编译时异常的处理方式2 抛出 (柳帅)");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
sdf.parse("2020-11-11");
}*/
}
运行时异常
另外还有一种异常是在程序运行时产生的,这种异常即使不编写异常处理代码,依然可以通过编译,因此被称为运行时异常,也称为unchecked异常。
RuntimeException类及其子类都是运行时异常。运行时异常的特点是在程序运行时由Java虚拟机自动进行捕获处理的,Java编译器不会对异常进行检查。
常见的运行时异常
| 运行时异常 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ArithmeticException | 算术异常 |
| IndexOutOfBoundsException | 索引越界异常 |
| ClassCastException | 类型转换异常 |
| NullPointerException | 空指针异常 |
| NumberFormatException | 数字格式化异常 |
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex01_ls_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例1_2】运行时异常 不处理 (柳帅)");
int[] arr = new int[3];
arr[0] = 1;
System.out. println(arr[3]);
}
}
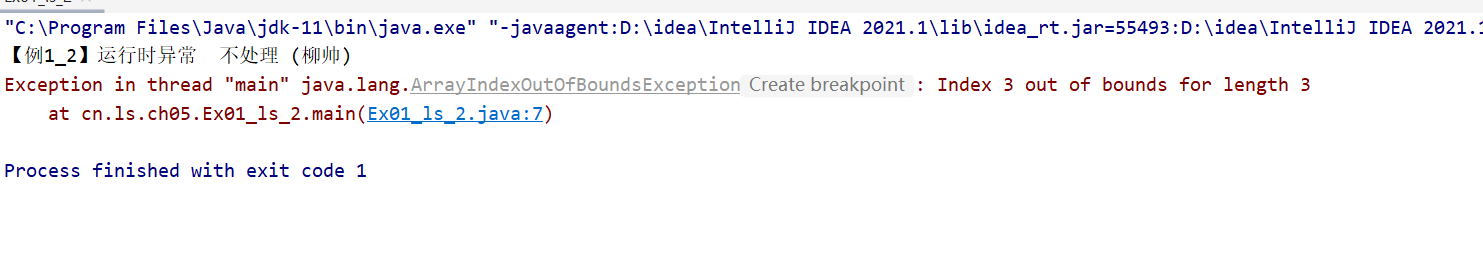
3. 异常处理及语法
3.1 异常的产生及处理
| 关键字 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| try | 里面放置可能引发异常的代码 |
| catch | 后面对应异常类型和一个代码块,该关键字表明catch块是用于处理这种类型的代码块 |
| finally | 主要用于回收在try代码块里打开的物理资源,如数据库连接、网络连接和磁盘文件。异常机制保证finally块总是被执行 |
| throw | 用于抛出一个实际的异常。它可以单独作为语句来抛出一个具体的异常对象 |
| throws | 用在方法签名中,用于声明该方法可能抛出的异常 |
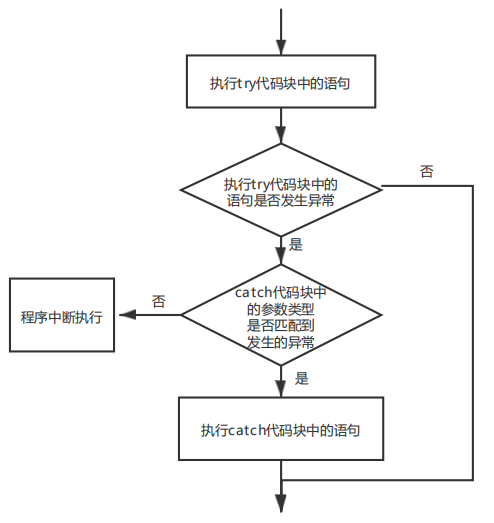
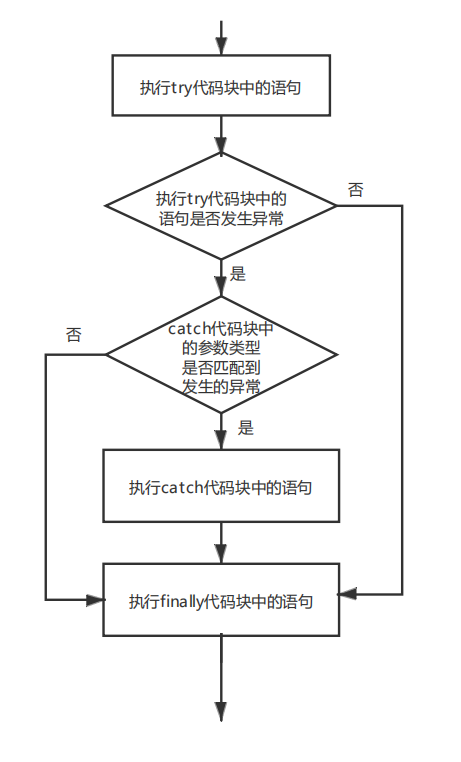
5.3.2 try...catch语句
try{
代码块
}catch(ExceptionType e){
代码块
}
try...catch语句编写注意事项
- (1)try代码块是必需的。
- (2)catch代码块和finally代码块都是可选的,但catch代码块和finally代码块至少要出现一个。
- (3)catch代码块可以有多个,但捕获父类异常的catch代码块必须位于捕获子类异常的catch代码块后面。
- (4)catch代码块必须位于try代码块之后。
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex02_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例2】try…catch捕获异常 (柳帅)");
//下面的代码定义了一个try…catch语句用于捕获异常
try {
int result = divide(4, 0); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) { //对异常进行处理
System.out.println("捕获的异常信息为:" + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("程序继续向下执行...");
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除
public static int divide(int x, int y) {
int result = x / y; //定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; //将结果返回
}
}

3.3 finally语句
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex03_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例3】try…catch…finallyh捕获异常 (柳帅)");
//下面的代码定义了一个try…catch…finally语句用于捕获异常
try {
int result = divide(4, 0); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) { //对捕获到的异常进行处理
System.out.println("捕获的异常信息为:" + e.getMessage());
return; //用于结束当前语句
} finally {
System.out.println("进入finally代码块");
}
System.out.println("程序继续向下…");
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除
public static int divide(int x, int y) {
int result = x / y; //定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; //将结果返回
}
}

4. 抛出异常
4.1 throws关键字 ---- 方法名后声明
在实际开发中,大部分情况下我们会调用别人编写的方法,并不知道别人编写的方法是否会发生异常。针对这种情况,Java允许在方法的后面使用throws关键字声明该方法有可能发生的异常,这样调用者在调用方法时,就明确地知道该方法有异常,并且必须在程序中对异常进行处理,否则编译无法通过。
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数1,参数2,…) throws 异常类1, 异常类2...{
方法体
}
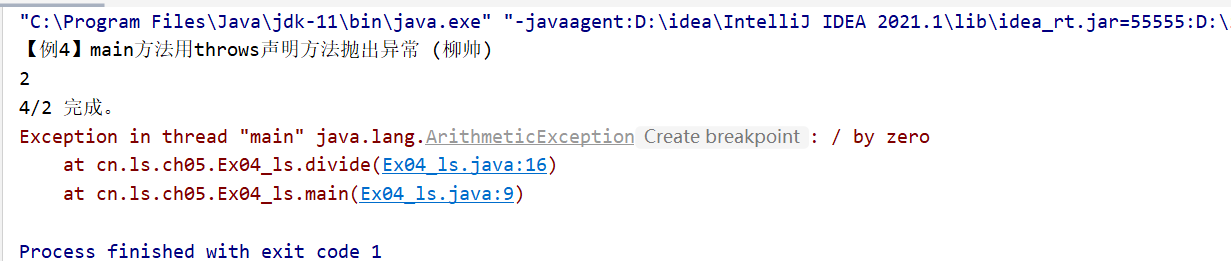
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex04_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("【例4】main方法用throws声明方法抛出异常 (柳帅)");
int result = divide(4, 2); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("4/2 完成。");
result = divide(4, 0); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println("4/0 完成。");
System.out.println(result);
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除,并使用throws关键字声明抛出异常
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws Exception
{
int result = x / y; //定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; //将结果返回
}
}
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex04_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("【例4】main方法用throws声明方法抛出异常 (柳帅)");
int result = divide(4, 2); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("4/2 完成。");
result = divide(4, 0); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println("4/0 完成。");
System.out.println(result);
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除,并使用throws关键字声明抛出异常
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws Exception
{
int result = x / y; //定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; //将结果返回
}
}
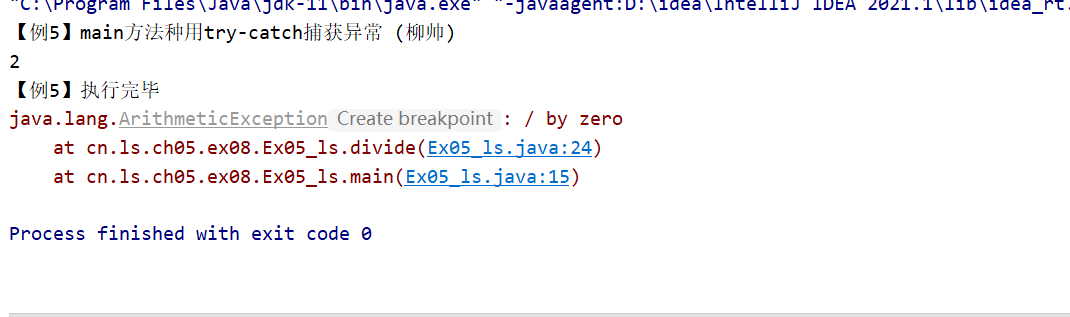
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex05_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例5】main方法种用try-catch捕获异常 (柳帅)");
//下面的代码定义了一个try…catch语句用于捕获异常
try {
int result = divide(4, 2); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
result = divide(4, 0); //调用divide()方法
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) { //对捕获到的异常进行处理
e.printStackTrace(); //打印捕获的异常信息
}
System.out.println("【例5】执行完毕");
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除,并使用throws关键字声明抛出异常
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws Exception {
int result = x / y; //定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; //将结果返回
}
}
4.2 throw关键字
在Java程序中,除了throws关键字,还可以使用throw关键字抛出异常。与throws关键字不同的是,throw关键字用于方法体内,抛出的是一个异常实例,并且每次只能抛出一个异常实例。
throw ExceptionInstance;
使用throw关键字抛出异常,通常有如下两种情况。
- (1)当throw关键字抛出的异常是编译时异常时,第一种处理方式是在try代码块里使用throw关键字抛出异常,通过try代码块捕获该异常;第二种处理方式是在一个有throws声明的方法中使用throw关键字抛出异常,把异常交给该方法的调用者处理。
- (2)当throw关键字抛出的异常是运行时异常时,程序既可以显式使用try…catch捕获并处理该异常,也可以完全不理会该异常,而把该异常交给方法的调用者处理。
package cn.ls.ch05;
public class Ex06_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例6】使用throw抛出异常 (柳帅)");
// 下面的代码定义了一个try…catch语句用于捕获异常
int age = 10;
try {
printAge(age);
} catch (Exception e) { // 对捕获到的异常进行处理
System.out.println("捕获的异常信息为:" + e.getMessage());
}
age = -1;
try {
printAge(age);
} catch (Exception e) { // 对捕获到的异常进行处理
System.out.println("捕获的异常信息为:" + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("【例6】执行完毕。");
}
// 定义printAge()输出年龄
public static void printAge(int age) throws Exception {
if(age <= 0){
// 对业务逻辑进行判断,当输入年龄为负数时抛出异常
throw new Exception("输入的年龄有误,必须是正整数!");
}else {
System.out.println("此人年龄为:"+age);
}
}
}

5. 自定义异常
Java允许用户自定义异常类,自定义的异常类必须继承自Exception或其子类。
package cn.ls.ch05.ex07;
class DivideByMinusException extends Exception{
public DivideByMinusException (){
super(); // 调用Exception无参的构造方法
}
public DivideByMinusException (String message){
super(message); // 调用Exception有参的构造方法
}
}
public class Ex_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("【例题7】自定义异常 除数负数异常 (柳帅)");
int result = 0;
try {
result = divide(4, -2);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (DivideByMinusException e) {// 对捕获到的异常进行处理
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 打印捕获的异常信息;
}
}
//下面的方法实现了两个整数相除
public static int divide(int x, int y) throws DivideByMinusException {
if(y<0){
throw new DivideByMinusException("除数是负数");
}
int result = x / y; // 定义一个变量result记录两个数相除的结果
return result; // 将结果返回
}
}

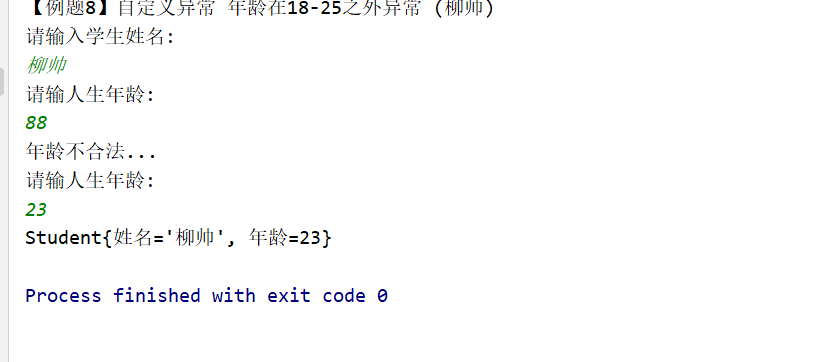
package cn.ls.ch05.ex08;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 自定义异常类,继承Exception及其子类
class 年龄超出范围Exception extends RuntimeException{
public 年龄超出范围Exception (){
super(); // 调用Exception无参的构造方法
}
public 年龄超出范围Exception (String 消息){
super(消息); // 调用Exception有参的构造方法
}
}
public class Ex_ls {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键盘录入学生信息:姓名,年龄封装成学生对象
//如果年龄在18-25之间,年龄合法,就可以封装,不在,重新录入
System.out.println("【例题8】自定义异常 年龄在18-25之外异常 (柳帅)");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生姓名:");
String name = sc.next();
Student stu = new Student() ;
stu.set姓名(name);
while (true){
System.out.println("请输人生年龄:");
int age = sc.nextInt();
try {
stu.set年龄(age);
break;
}catch (RuntimeException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
System.out. println(stu) ;
}
}
class Student{
private String 姓名;
private int 年龄;
public String get姓名() {
return 姓名;
}
public void set姓名(String 姓名) {
this.姓名 = 姓名;
}
public int get年龄() {
return 年龄;
}
public void set年龄(int 年龄) {
if (年龄 < 18 || 年龄 > 25){
throw new 年龄超出范围Exception("年龄不合法...");
}else{
this.年龄 = 年龄;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"姓名='" + 姓名 + '\'' +
", 年龄=" + 年龄 +
'}';
}
}
idea 改变注释颜色
1.进入设置。File->Setings
2.进入编辑器设置。Editor
3.进入色彩方案设置。ColorScheme
4.进入默认语言设置。Lauage Defaults
5.进入注释设置。Comments
6.前景色设置即注释字体颜色设置。Foreground